When we think about the cells in our bodies, we can imagine tiny, bustling cities where various components work together to keep everything running smoothly. Among these components, mitochondria are often called the "powerhouses" of the cell. But what exactly does this mean? Let's break it down in simple terms.
What Are Mitochondria?

Mitochondria are small, membrane-bound structures found within most of our cells. They have a unique structure with an outer membrane and a highly folded inner membrane. These folds, called cristae, increase the surface area inside the mitochondria, allowing them to be very efficient at their job.
The primary function of mitochondria is to produce energy. They do this by converting the energy stored in food molecules into a form that cells can use. This process is known as cellular respiration, and it involves a series of complex chemical reactions.
Inside the mitochondria, glucose undergoes several chemical reactions. The key part of this process is the production of a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
ATP - The Energy Currency
• Energy Storage: ATP stores energy in its chemical bonds, specifically in the bond between its second and third phosphate groups.
• Energy Release: When a cell needs energy, it breaks this bond, converting ATP into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and a free phosphate molecule. This reaction releases energy that the cell can use for its activities
• Energy Utilization: The energy released from ATP is used for various cellular functions such as:
• Muscle Contraction: Muscles use ATP to contract and move.
• Active Transport: Cells use ATP to transport molecules across their membranes against a concentration gradient.
• Chemical Synthesis: ATP provides the energy required to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones.

Boosting Mitochondrial Efficiency
To keep our bodies energized and functioning optimally, it's important to support the health and efficiency of our mitochondria.
- Regular Exercise
- Balanced diet with minimally processed foods
- Adequate Sleep
- Stay Hydrated
- Reduce Stress
- Minimize exposure to environmental toxins (pollutants, alcohol, smoking, chemicals)
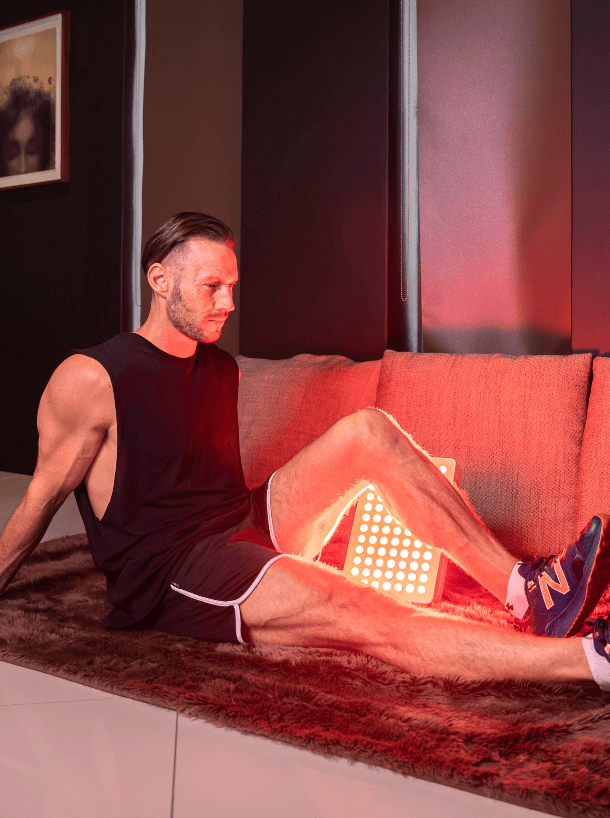
- Red Light Therapy

In A Nutshell
Mitochondria contain light-sensitive molecules called chromophores. The light absorption of mitochondria from red light exposure enhances the activity of an enzyme called cytochrome c oxidase, which is part of the electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain is a series of reactions in the mitochondria that ultimately leads to the production of ATP. With increased activity of the electron transport chain, the mitochondria can produce more ATP.
Red light therapy has been featured in thousands of clinical studies, and is proven to:
• Improve energy levels
• Increase sleep quality
• Speed up muscle recovery
• Decrease inflammation
• Improve skin complexion
...and much more
Conclusion:
With so many benefits of red light therapy being analysed and proven in the thousands of clincal studies performed, there is one common takeaway - there are no negative side effects of this holistic treatment.
And if you're ever needing to know why to choose a Mychondria device over any other brand, check this article below: