It's very common for a health product to promise you a world of benefits, only to let you down when you purchase it.
Many companies will take advantage of the fact that you, as a health minded individual, will try any product at least once in order to see if it works for you.
With an extensive list of benefits, red light therapy can easily come across as another one of these products.
Let's be honest, when you read "improved sleep, faster muscle recovery, decreased inflammation, and more!", you might think that red light therapy is another one of these gimmicks.
How could a simple form of light therapy really offer so many benefits?
In this blog post we are going to unpack the basic mechanism by which red light therapy works, so that you can have a better understanding of how red light therapy is able to achieve such profound effects.
A Quick Biology Refresher
To start, we are going to cover some basics which will be fundamental to understanding how red light therapy works.
Don't worry though, we won't be using an endless list of big terms in order to try sound clever. We are going to keep this to the fundamentals, so that anyone can understand how red light therapy works.
The Mitochondria

No doubt you have already heard the term mitochondria. These are the little powerhouses within every one of your cells. They generate the energy currency, often referred to as ATP, which your cells need in order to perform their function.
The mitochondria are like the power stations in a city. Although different cities may have completely different functions, such as paper production, or medical research, all of them will require an efficient power station in order to function properly.
In this same way, any cell of yours, be that a skin cell, muscle cell, or brain cell, will require efficient mitochondria in order to function properly.
Any cell that has more energy is going be able to perform its specific function better.
Muscle cells can repair themselves faster.
Skin cells can produce more collagen.
Hair cells can build stronger hair follicles.

Light And Your Mitochondria
Within your mitochondria there is an enzyme, called cytochrome c oxidase (CCO). This enzyme is responsible for the last part of the reaction to create energy within your cells.
The interesting part about CCO is that it can absorb certain frequencies of light as energy.

It turns out that the type of light that is best absorbed by CCO is in the red and near-infrared range of light, most efficiently in the mid 600-700nm and 800-900nm range,
When red and near-infrared light hits CCO, it stimulates an increase in energy production within your cells.
This is the exact mechanism by which red light therapy gives you such profound benefits.
How Much Light Do Your Cells Need To Get These Benefits?
It turns out that different cells require different amounts of light in order to have beneficial effects.
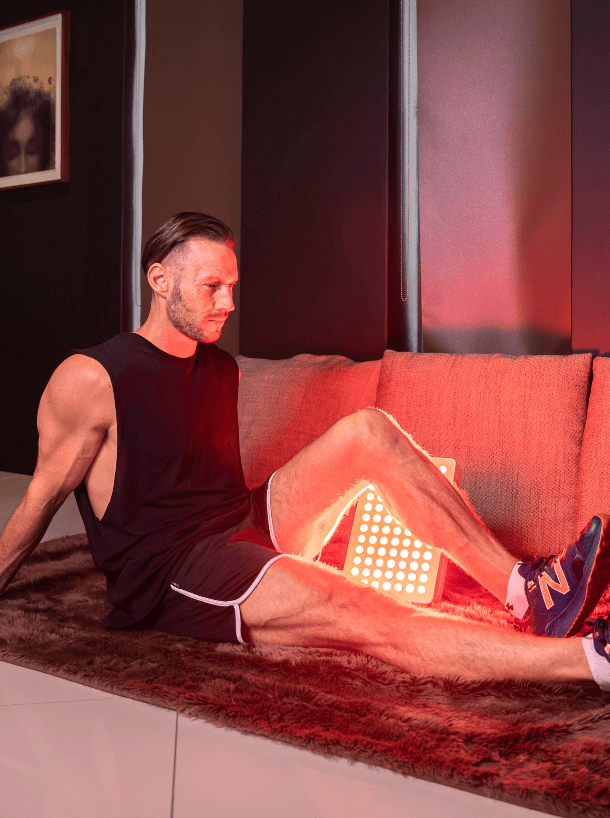
Superficial cells, such as skin and muscle cells, require much lower doses than deeper cells, such as organ and joint cells.
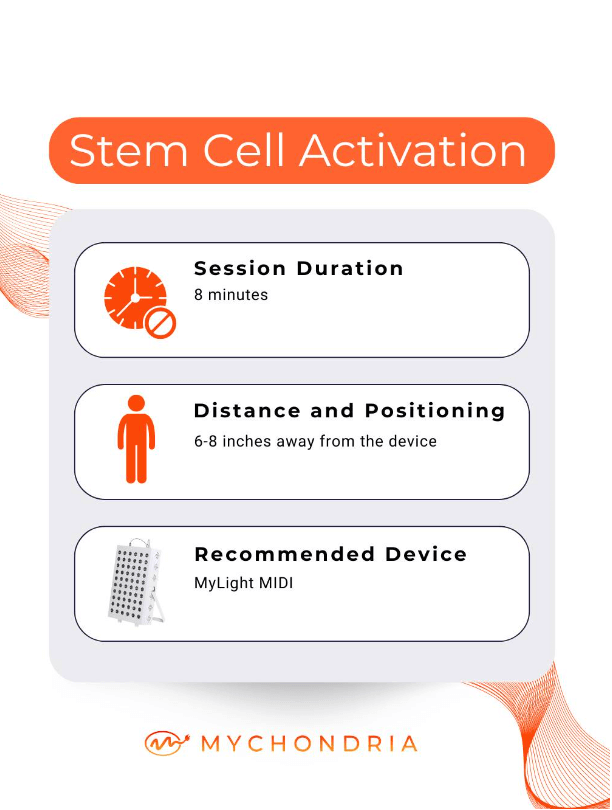
This can mean a dosage anywhere between 5-60+ J/cm2 (a measurement of light energy).
The time it takes to get this amount of light energy will depend on the strength of the red light therapy device you are using.
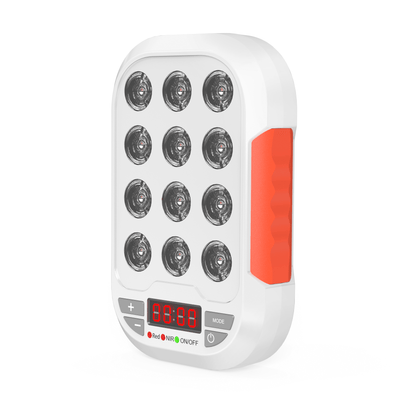
The MyLight MIDI, one of the most powerful devices on the market, delivers around 6.5 J/cm2 every minute!

This means you can get incredible benefits in as little as 5-10 minutes with this device, whereas with a cheaper device you may require 30+ minutes in order to achieve this.
If you're ready to upgrade your health and performance, then be sure to checkout the MyLight devices below:
View The MyLight Collection >>>
Written by Nick Coetzee